ABOUT SHIMADZU
History of Shimadzu
Since succeeding in Japan's first manned balloon flight, Shimadzu has, with an inexhaustible spirit of inquiry, continued to open up new frontiers in science and technology. In 1877, Genzo Shimadzu Sr. became the first person in Japan to succeed in making a manned balloon. Inherited by subsequent generations, his frontier spirit has since spread all over the world, and has given birth to a broad range of pioneering, cutting-edge instruments.

A print of the hydrogen balloon built by Genzo Shimadzu Sr.
Genzo Shimadzu Sr. (the founder)
Born in 1839 in Kyoto, the second son of Seibei Shimadzu, a maker of Buddhist altars. In 1875, inspired with the idea of raising the profile of science in Japan, he left the family business and started to manufacture physical and chemical instruments for educational purposes in Kiyamachi-Nijo.

Genzo Shimadzu Jr
Born in 1869 in Kyoto, the first son of Genzo Sr. His childhood name was Umejiro but with the sudden death of his father in 1894, he became head of the family and assumed the name of his father. During his lifetime he was credited with 178 inventions and was chosen as one of the ten greatest inventors of Japan.

Spirit for research in science and technology developed to medical imaging
In 1896, only a few months after Dr. Conrad Roentgen‘s discovery of X-rays, Genzo Shimadzu Jr. and Professor Muraoka of Kyoto University succeeded in taking the first X-ray images in Japan. With this pioneering discovery, another foundation was laid for a variety of future developments for imaging systems in medicine:
1896
Succeeded in taking X-ray pictures (first in Japan).
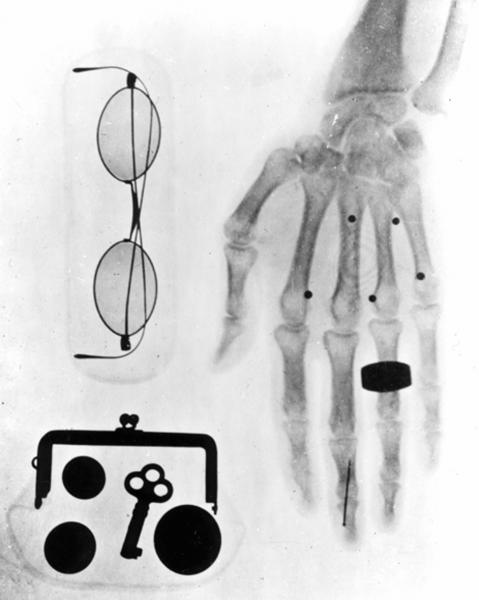
1911
Large-size medical X-ray apparatus
Japan's first large X-ray apparatus using AC power. An induction coil-type of X-ray apparatus with a rectifier to convert AC to DC, it was installed at the Ohtsu Hospital of the Japanese Red Cross Society.

1918
X-ray apparatus Diana
Mechanical full-wave rectification system, with a capacity of 120kVp and 100mA. Dominated Japan's radiography industry at that time.

1922
Deep therapy apparatus Jupiter
Mechanical rectification type provided with two main transformers and two rectifiers.

1937
Diagnostic X-ray apparatus Katsura and Hokoku
These units conformed to the laws relating to shockproof and X-ray proof specifications. The X-ray tube was cooled by oil circulating in a tank, and the high voltage generator was enclosed in the oil tank together with the rectifier and the transformer. This was a full-wave rectification system.

1961
World's first remote-controlled X-ray TV system
Control of all operations was possible from another room, and the radiologist was protected from the risk of exposure. World's first system.

1980
PANGIOMAX
Completion of a stereoscopic magnification system for cerebral and abdominal angiography.

1996
Cvision
Development of a multi-functional digital R/F C-arm table.
2003
HeartSPEED
The first (digital cardiac) system in the world incorporating a direct conversion flat panel detector.
2005
MobileDaRt
The first fully digital mobile X-ray system in the world, equipped with a portable flat panel detector.
2007
SUREengine
Introduction of a high-speed digital image processing engine. This new cutting-edge technology generated a new level of fluoroscopic image quality.
A more detailed listing of Shimadzu history is available on our global website:
Shimadzu Visionary
An introduction to the Foundation Memorial Hall, based on the technologies and events that mark each era, and chronicled by date:

Shimadzu Foundation Memorial Hall
Located at the northern end of the Takase River, the Kiyamachi-Nijo district (Japan) is the birthplace of the Shimadzu Corporation and a place where visitors can experience the atmosphere and history of Shimadzu's early years through story and theme-based exhibits.
Read more about the Foundation Memorial Hall:

A driving force in medical imaging technology, Shimadzu introduced many industry firsts which meanwhile have become standard in today’s clinical applications.
Shimadzu applies to the highest standards to ensure sophisticated and reliable product solutions to our users.
Intelligent concepts have been developed
- offering customized system solutions,
- creating improved working and workflow conditions,
- providing patient-friendly and safety features,
- improving clinical results with reduced radiation exposure.